In what place are fats amassing?
Different Distribution is connected to cardiometabolic risk in a method.
Differences In human anatomy compositions between women and men have been unravelled in this book in Biology of Gender Differences. Taking benefit of anatomic and functional imaging methods, a light shines on tweaks of supply, and connect them amongst genders with different risk.
It is no Surprise that women and men have different body compositions, together with women – the human body type – along with men accumulating fat from the gut with a physique that is pear-shape, using extremity mass. However, can those differences influence upon the wellbeing of women and men?
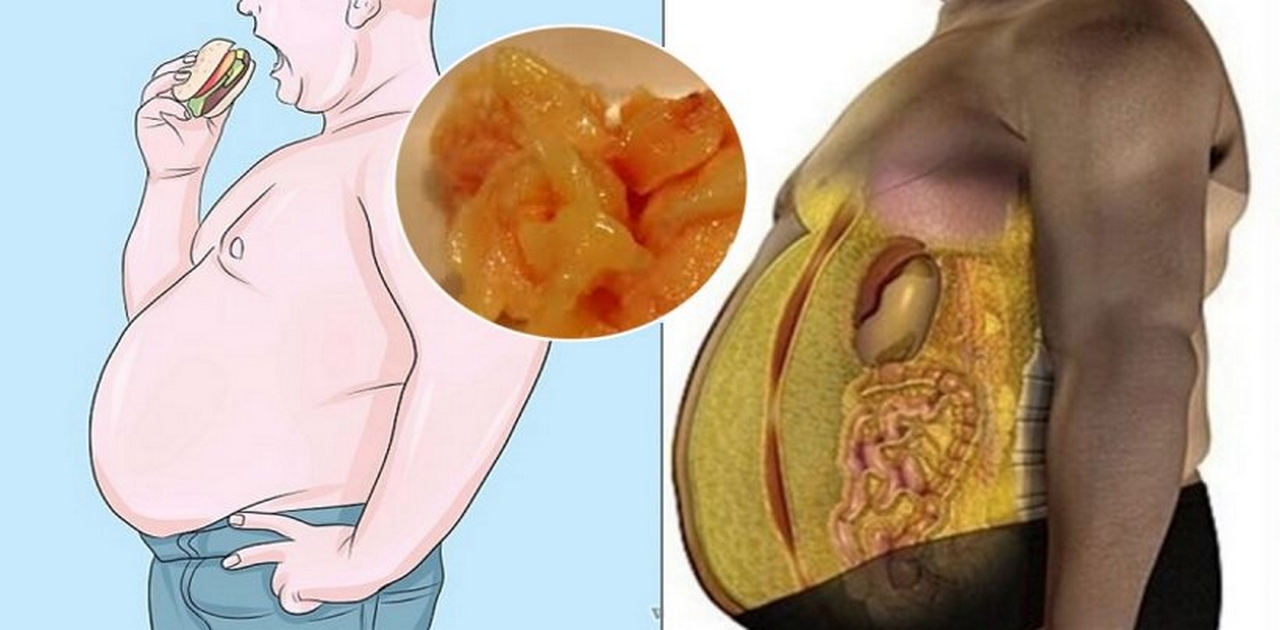
Even though Women and men are susceptible to obesity, medical consequences tend to be different between the genders, even if additional components, such as overall fat mass or body mass index (BMI) are alike.
This Monitoring led the authors with the novel of Biology of Gender Differences to think about people signs, like fat mass and the BMI enough to guarantee a suitable comprehension of the hazard between women and men.
Employing a Unique mixture of anatomic and functional imaging methods, Schorr et al.. Of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School could run fat deposits at a cohort of both women and men and a close analysis of human body makeup with BMI and age. Their findings support the hypothesis that those differences have a better affect cardiometabolic risk than excess that is overall.
The overall Apple versus pear human body contour gap was validated, since women were found to possess lower extremity fat in comparison with men, who’ve visceral fat tissue (VAT). The complete mass was high in women than men.
At comparable BMI and age, but the phenotype was correlated with a hazard profile that was damaging. The pear structure, together with fat collected in the body, led in an protective element.
But, Inspite of the chance of disorder being higher in men compared to women the growth in risk is significantly greater in women than men since the BMI increases.
The usage of Dualenergy xray Absorptiometry, Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy to check fat pockets, for example muscle tissue, lean and lipids helped to comprehend the reasons.
Even though Women have significantly less visceral adipose tissue (VAT) over all, VAT accumulation in girls pose a greater cardio-metabolic hazard in contrast to men.
Men too Demonstrated higher intrahepatic (IHL) and intramyocellular lipids (IMCL) than women, using IMCL being fully a distinct detrimental element for men as opposed to women.
The Presence of lean mass has been shown to be protective in the genders, indicating an increase of muscular tissue can counter act the impacts of the depots that were visceral though the mass doesn’t change.
In Conclusion, We can view how human body makeup impacts the risk in an manner: the man that is detrimental has been IMCL for adult guys, while VAT can be a big risk factor for ladies, although men tend to be somewhat more vulnerable general.
The Mechanics are to elucidate, however, determinants and also gender stimulation could reflect key players.
What it’s Sure is the fact the chances opened by the growth of technologies and strategies are a step towards a comprehensive comprehension of risk connected with fat supply.
What Exactly Is Left to accomplish? The writers assert of verifying the causality of the Value Sex gaps and cardiometabolic risk-differences, and we’re currently waiting to see Depots will result in higher prevalence of disorder Between women and men.
